Agribusiness, Agriculture, Veterinary Medicine, Cassava, Garri, food security, Agritech and the Red Meat Value Chain.
Friday, July 20, 2018
Cows and pigs are great livestock, but they can also make you really sick
Cows and pigs are great livestock, but they can also make you really sick.Sometimes in this world, it’s the little things that can cause the most problems. Really, really little things.
This is especially true for anyone working around or with livestock in Maine, according to Dr. Anne Lichtenwalner, director of the University of Maine Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory and associate professor of animal and veterinary science.
Some farm animals can actually “share” parasites with their human companions. “There are actually just a handful of parasites that I worry about,” Lichtenwalner said. “These are critters that are parasites that can live inside you and tend not to be fatal, but that can cause some ugly surprises.”
The two most common zoonotic parasites — those that can transfer from animals to humans — in Maine are Ascaris suum and Cryptosporidium. “You are protected by your innate and acquired immune system,”
How animal parasites find a home in humans.
How animal parasites find a home in humans. There has been a lot of buzz recently about a video shared by Oregon woman Abby Beckley, who describes removing worms from her eye. Researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released a case report documenting Beckley’s infection as the first human case of the cattle eyeworm Thelazia gulosa.
We certainly feel for Beckley having to go through this ordeal, and without a doubt, felt our skin crawl just thinking about it. But aside from the “creep” factor of this case, it does makes us wonder how a cow parasite ever ended up in a human eye. And it begs the more fundamental question: How are animal parasites able to infect humans?
To answer this question, we need to understand more about parasites and their ecology. As a veterinarian and disease ecologist, my research examines what ecological factors influence the emergence of zoonoses — diseases that spread from animals to humans. The case of the cattle eyeworms is certainly intriguing.
Transmission of parasites from one host to another can occur through several routes, depending on where the parasite resides in the host and how it is shed, for example through feces, blood or other bodily secretions. Direct contact, consumption of contaminated water or food (Cryptosporidium, Giardia), or via a vector like a tick or mosquito are all possible. Parasitic infections transmitted from animals to humans have occurred naturally throughout history.
Bacteria carried by unneutered dogs could put pregnant women at risk.
Bacteria carried by unneutered dogs could put pregnant women at risk. Intact dogs can carry Brucella canis bacteria, which can cause flu-like symptoms in people and pose risk to a pregnancy, according to a study in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Brucellosis infections can cause miscarriages in animals and are associated with fetal problems in pregnant women, and the CDC says pregnant women who may have been exposed to the bacteria should consult their health care provider.
A bacteria carried by dogs that haven't been neutered can produce flu symptoms in humans and potentially jeopardize a pregnancy, a new study suggests. Brucellosis infection is most commonly spread by livestock like sheep, cattle, goats and pigs. But a strain of the bacterium carried by dogs -- Brucella canis -- could be widespread in humans, warned lead researcher Martha Hensel, a veterinarian with Texas A&M University.
B. canis is carried by dogs that can still reproduce, Hensel noted. It's not clear exactly how the bacteria might spread to humans, but it's most likely passed through contact with reproductive organs or urine.
People who regularly handle such dogs -- vets, dog shelter employees, dog breeders -- are most at risk for contracting brucellosis, Hensel said. However, pet ownership is a likely risk factor for infection, particularly for young children and people with compromised immune systems, Hensel and her colleagues explained.
The researchers highlighted some case studies:
1) A 3-year-old New York City girl came down with brucellosis in 2012 after exposure to an infected puppy recently purchased from a pet store.
2)Several people with HIV have developed brucellosis in recent years, all linked to intact dogs they owned that were later diagnosed with B. canis infection. more
Tuesday, July 10, 2018
'Green'-feed: Industrial microbes could feed cattle, pigs, chicken.
'Green'-feed: Industrial microbes could feed cattle, pigs, chicken. Deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity loss and nitrogen pollution . Today's agricultural feed cultivation for cattle, pigs and chicken comes with tremendous impacts for the environment and climate. Cultivating feed in industrial facilities instead of on croplands might help to alleviate the critical implications in the agricultural food supply chain.
Protein-rich microbes, produced in large-scale industrial facilities, are likely to increasingly replace traditional crop-based feed. A new study now published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology for the first time estimates the economic and environmental potential of feeding microbial protein to pigs, cattle and chicken on a global scale. The researchers find that by replacing only 2 percent of livestock feed by protein-rich microbes, more than 5 percent of agricultural greenhouse gas emissions, global cropland area and global nitrogen losses could each be decreased.
Monday, July 9, 2018
How to detect foot and mouth disease with simple environmental sampling.
How to detect foot and mouth disease with simple environmental sampling. Simple sampling method eases identification of foot and mouth disease outbreaks.
Sampling the environment is an effective way to detect foot and mouth disease, according to a paper published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The sampling method, swabbing environmental surfaces where livestock are kept, can be easily performed and can detect viral genetic material that can persist in the environment well beyond the time when livestock cease manifesting clinical signs of disease.
Unlike taking clinical samples, those taking samples need not be able to recognize clinical signs of foot and mouth disease. Thus, smallholder farmers in developing countries could take the samples in lieu of veterinarians.
Foot and mouth disease is caused by a member of the genus, Aphthovirus. It causes blisters in the mouths and on the feet of cattle, goats, pigs, and other cloven-hoofed mammals. The virus contains a single strand of RNA that encodes its genome.
Humans are not susceptible to foot and mouth, and the disease generally doesn't kill animals. However, it can greatly reduce milk and meat production, creating a hardship for smallholder farmers.
Foot and mouth disease can also have a major impact on a national economy.
In foot and mouth disease-free countries, an incursion of foot and mouth disease can cause significant losses due to imposed grade restrictions and subsequent control measures required to eradicate the disease.
Bacteria-powered solar cell converts light to energy, even under overcast skies.
Bacteria-powered solar cell converts light to energy, even under overcast skies.University of British Columbia researchers have found a cheap, sustainable way to build a solar cell using bacteria that convert light to energy. Their cell generated a current stronger than any previously recorded from such a device, and worked as efficiently in dim light as in bright light.
This innovation could be a step toward wider adoption of solar power in places like British Columbia and parts of northern Europe where overcast skies are common. With further development, these solar cells -- called "biogenic" because they are made of living organisms -- could become as efficient as the synthetic cells used in conventional solar panels.
Transmission of NDM bacteria between dogs and humans established.
Transmission of NDM bacteria between dogs and humans established.The transmission of NDM bacteria between dogs and humans has been established for the first time. In 2015, a New Delhi-metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM) Escherichia coli bacteria was discovered in two Finnish dogs.
An article recently published in the journal Eurosurveillance reveals that the dogs' owner did also carry the bacterium. This is presumably the first time in the world that the transmission of NDM-bacteria between a dog and a human has been reported.
The NDM-bacteria that had originally been isolated from ear specimens from two dogs in the same family initiated an investigation about the spread and origin of the bacteria. Specimens were also taken from family members and the dogs. The relatedness of the bacteria were investigated by examining the nucleotide sequence of their genome. The study was a collaboration between the University of Helsinki, the National Institute of Health and Welfare, and the Finnish Food Safety Authority Evira.
Sunday, July 8, 2018
Tweets show daily rhythm of our thinking.
Tweets show daily rhythm of our thinking. A study of 800-million tweets finds distinct daily cycles in our thinking patterns. Our mode of thinking changes at different times of the day and follows a 24-hour pattern, according to new findings published in PLOS ONE. University of Bristol researchers were able to study our thinking behaviour by analysing seven-billion words used in 800-million tweets.
Researchers in artificial intelligence (AI) and in medicine used AI methods to analyse aggregated and anonymised UK twitter content sampled every hour over the course of four years across 54 of the UK's largest cities to determine if our thinking modes change collectively.
The researchers revealed different emotional and cognitive modalities in our thoughts by identifying variations in language through tracking the use of specific words across the twitter sample which are associated with 73 psychometric indicators, and are used to help interpret information about our thinking style.
Neuroscientists uncover secret to intelligence in parrots.
Neuroscientists uncover secret to intelligence in parrots. Neuroscientists have identified the neural circuit that may underlay intelligence in birds, according to a new study. The discovery is an example of convergent evolution between the brains of birds and primates, with the potential to provide insight into the neural basis of human intelligence.
"An area of the brain that plays a major role in primate intelligence is called the pontine nuclei," explained Cristian Gutierrez-Ibanez, postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Psychology. "This structure transfers information between the two largest areas of the brain, the cortex and cerebellum, which allows for higher-order processing and more sophisticated behaviour. In humans and primates, the pontine nuclei are large compared to other mammals. This makes sense given our cognitive abilities."
Birds have very small pontine nuclei. Instead, they have a similar structure called the medial spiriform nucleus (SpM) that has similar connectivity. Located in a different part of the brain, the SpM does the same thing as the pontine nuclei, circulating information between the cortex and the cerebellum. "This loop between the cortex and the cerebellum is important for the planning and execution of sophisticated behaviours," said Doug Wylie, professor of psychology and co-author on the new study.
Mothers who follow five healthy habits may reduce risk of obesity in children.
Mothers who follow five healthy habits may reduce risk of obesity in children. Children and adolescents whose mothers follow five healthy habits which are eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, keeping a healthy body weight, drinking alcohol in moderation, and not smoking .
These are 75% less likely to become obese when compared with children of mothers who did not follow any such habits, according to a new study led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
When both mother and child adhered to these habits, the risk of obesity was 82% lower compared with mother and children who did not.
One in five children in the U.S aged 6-19 have obesity, putting them at risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic conditions later in life. While it is known that genetics play a role in obesity, the rapid increase of the disease in recent years is likely due to changes in lifestyle and diet, indicating that "nurture" more than "nature" is fueling the current obesity epidemic.
Vaccination increases family wealth, girls' education.
Vaccination increases family wealth, girls' education.A Washington State University-led research team found households in rural Africa that vaccinate their cattle for East Coast fever increased their income and spent the additional money on food and education. Researchers also found that when fewer cattle died from the fever, girls were more likely to attend secondary school.
"When households vaccinate, it increases their wealth and income and sets them on a trajectory to provide education for their children," said lead author Tom Marsh, professor in WSU's School of Economic Sciences and the Paul G. Allen School for Global Animal Health. "Vaccinating is a way for households to pull themselves out of poverty.
Cattle may spread leptospirosis in Africa.
A study has shown that cattle may spread leptospirosis in Africa. The bacterial infection leptospirosis is increasingly recognized as an important cause of fever in Africa. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have analyzed the major risk factors for contracting leptospirosis and discovered that rice and cattle farming are associated with acute infection.
Leptospirosis, caused by bacteria of the genus Leptospira, causes a wide range of symptoms and can lead to serious complications include kidney and liver problems. In one study conducted in northern Tanzania, 8.8% of people with severe fevers had leptospirosis. Scientists know that animals can carry leptospirosis and lead to its spread throughout the environment or directly to humans. However, the major animal reservoirs and modes of transmission have not been well described.
Rice farming, cleaning cattle waste, feeding cattle and farm work were all positively associated with acute leptospirosis. Smallholder farming -- which may be associated with substantial exposure to both livestock and rodents -- as well as frequent sightings of rodents in one's kitchen or food store -- was associated with seropositivity. see
Benefits Of Coconut Oil For Dogs And Cats.
Benefits Of Coconut Oil For Dogs And Cats. . The benefits of coconut oil are enormous and have found usefulness in both animals and man.
Coconut oil also contains lauric acid, a saturated fatty acid that is converted in the body to monolaurin, a monoglyceride compound with numerous beneficial properties, such as anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-microbial, anti-fungal and anti-protozoal.
Coconut oil also contains lauric acid, a saturated fatty acid that is converted in the body to monolaurin, a monoglyceride compound with numerous beneficial properties, such as anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-microbial, anti-fungal and anti-protozoal.
Saturday, July 7, 2018
Shorter rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) schedule safe and effective.
Shorter rabies PrEP schedule safe and effective. In healthy participants, intradermal administration of a double dose of rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, given during two clinic visits was safe and noninferior to a standard three-visit schedule, according to recent data.
Given the efficacy of the shortened schedule, which may result in wider acceptance, Patrick Soentjens, MD, PhD, head of the travel clinic at Queen Astrid Military Hospital’s center for infectious diseases in Brussels, and colleagues said intradermal (ID) administration of a two-dose, two-visit PrEP regimen is now one of the first-line schedules recommended by the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization for international travelers and individuals at risk for rabies in endemic countries.
“Rabies represents an unremitting and neglected global challenge. As such, new shortened ID schedules aim to be cost-, dose- and time-sparing, while maintaining safety and effectiveness,” the researchers wrote in Clinical Infectious Diseases. “Shortened PrEP ID schedules, using simpler low-dose vaccine regimens, can be considered an illustration that less can be more.”
Ichthyosis : a severe skin disease that affects dogs and humans.
Ichthyosis : a severe skin disease that affects dogs and humans.Both dogs and humans can suffer from ichthyosis, a disorder in which the skin becomes very dry, scaly, and prone to secondary infections. Medical researchers have uncovered new details about one form of the disease and took a step toward developing a topical therapy.
A particularly serious skin barrier condition is known as ichthyosis in which thick layers of scales can build up. It arises when the lipid-synthesis process in the skin goes awry. Besides causing discomfort and a scaly appearance, the condition can make the skin prone to secondary infections.
No effective treatments currently exist for ichthyosis, but a new study led by pathologist Elizabeth Mauldin of Penn's School of Veterinary Medicine takes a step toward a topical therapy.Using dogs that were born with one form of the disease, she and her colleagues uncovered its cellular and metabolic basis and used that information to create a compound to address the lipid deficits seen in the disease.
Using a lotion applied to the skin, they were able to reinstate the corneocyte lipid envelope (CLE) that is typically lacking in these patients. Ichthyosis : a severe skin disease that affects dogs and humans.
Unraveling the genetics of disc disease in dogs.
Unraveling the genetics of disc disease in dogs.Since the early 1900s, veterinarians have observed intervertebral disc disease -- a common cause of back pain, rear limb paralysis and inability to walk -- more frequently in dogs with short legs (dachshund, French bulldog, and Pekingese to name a few.) But they couldn't pinpoint why? until now. Why short-legged dogs more likely to develop painful disease.
University of California, Davis, researchers reveal the discovery of a genetic mutation across breeds that is responsible for chondrodystrophy (the skeletal disorder leading to shorter legs and abnormal intervertebral discs) in a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Dogs with intervertebral disc disease (IVDD) are 50 times more likely to have this mutation; that's an incredibly strong correlation with disc disease," said Danika Brannasch, a veterinary geneticist and the paper's senior author. "Being able to identify the cause of this painful condition is the first step to alleviating pain and suffering for dogs at greatest risk."
Dogs with noise sensitivity should be routinely assessed for pain by veterinarians.
Dogs with noise sensitivity should be routinely assessed for pain by veterrinariians.Dogs which show fear or anxiety when faced with loud or sudden noises should be routinely assessed for pain by veterinarians, according to new research.
Researchers believe that pain, which could be undiagnosed, could be exacerbated when a noise makes the dogs tense up or 'start', putting extra stress on muscles or joints which are already inflamed leading to and associated with a loud or startling noise.
Animal behavioural scientists from the UK and Brazil examined cases of dogs which had developed a sensitivity to either loudness, different pitches, or sudden noises, and found that those which also had associated musculoskeletal pain formed a greater sensitivity to noise. The study suggested that that fear or anxiety about noise could be association between a fear of noises and underlying pain.
7 Powerful Health Benefits of Glutathione.
Glutathione is a detoxifier that is found naturally in your body's cells. It eliminates certain dangerous toxins and is also a powerful antioxidant. Glutathione is an antioxidant that fight cell damage that can be caused by certain chemical reactions,these chemical reactions release free radicals, which can damage cells within the body.
The body produces glutathione naturally but this process wanes with age,hence conscious efforts must be made to boost the level of glutathione to enjoy all the health benefits. These chemical reactions produce substances known as free radicals, which can damage cells. Glutathione can be sourced naturally from fruits and vegetables such as potatoes, peppers, carrots, onion, broccoli, avocados, squash, spinach, garlic, tomatoes, grapefruit, apples, oranges, peaches bananas and melon.
Glutathione levels can be boosted by using certain supplements to enjoy the benefits.
1) Increases Energy Levels.
2)Strengthens the Immune System.
3)Reduces Muscle & Joint Discomfort.
4)Improves Mental Focus & Clarity.
5)Helps the Liver Detoxify the Cells.
6)Improves Quality of Sleep
7)Slows Down the Aging Process.
Friday, July 6, 2018
Synthetic meats are on their way, and our farmers are going to be left behind.
Synthetic meats are on their way, and our farmers are going to be left behind.Fake’ animal proteins are set to disrupt world markets – and much faster than our agriculture industry is anticipating, argues food strategist Dr Rosie Bosworth.
Benefits of glutathione.
Benefits of glutathione.
Glutathione; 1) Is the Body's Master Antioxidant it is considered the master antioxidant due to its unique multifunctional characteristics as well as it's unprecedented ability to neutralize many types of free radicals that assault the cell. It is the only antioxidant that recycles itself again and again to continue fighting free radicals.
2) Is The Primary Detoxifier of the Cell
Today we are confronted by over 80,000 chemicals in the air we breathe, the food and water we ingest, and the materials we touch and handle. Many of these toxic chemicals enter our cells and must be eliminated to protect the cell and maintain optimum function. Glutathione is the cell's first line of defense against chemicals and toxins and the primary detoxifier that can eliminate many of these toxins when it is present in optimal amounts.
3)Is A Powerful Chelator of Heavy Metals
Heavy metals enter our cells in the same manner as chemical toxins. Fortunately, they can be removed from the cell by a process of chelation, and Glutathione is one of the cell's most powerful chelating agents.
4) Is The Protector of the Immune Cell
Our immune cells are designed to protect us, but what protects the immune cell? Glutathione is the protector of the immune cell and allows newly formed immune cells to proliferate to attack germs and viruses.
5) Is The Protector of Mitochondrial DNA
The breakdown of the mitochondrial DNA accelerates aging and increases cell death. Glutathione is the protector of the Mitochondrial DNA, and the lower the glutathione level, the more vulnerable this DNA becomes to breakage.
6) Is The Protector of the Nucleus of the Cell
The nucleus of the cell regulates all cell activity and protecting it is critical to the health of the cell and its optimal function. When present in abundance, glutathione gives the nucleus the protection it needs.
7) Reduces Oxidative Stress
Oxidative Stress is the most aggressive destructive force that assaults the cell. Cells manufacture a number of antioxidants to counter oxidative stress. Glutathione plays a primary role in neutralizing many different types of free radicals.
Cellgevity offers Superior Glutathione Support .
Cellgevity offers Superior Glutathione Support. Glutathione has been extensively studied by medical science, with more than 98,000 studies recorded in the official U.S. medical library. Among the findings of these studies are that people with high levels of glutathione have increased energy, healthy sleep patterns and improved immune systems. In addition, these same people benefit from improved mental clarity, and they are found to live longer lives of greater quality than those with low levels of glutathione.
Glutathione is more necessary than ever due to the environment in which most people live. Scientists have counted over 80,000 foreign chemicals in the foods people ingest and the air that is breathed. Without glutathione, all of these toxins can enter the body's cells and play havoc with their health.
Some of the most dangerous of the toxins that can enter the body are heavy metals. Fortunately, glutathione can remove heavy metals from the body's cells through a process called chelation. Although glutathione is not considered an essential nutrient, it is a naturally produced enzyme that plays a significant role in human health. Glutathione is considered the most effective natural antioxidant, and increased levels of the enzyme can greatly reduce aging and the progression of age-related diseases.
Toxins also break down mitochondrial DNA within the cells. This causes rapid aging and premature cellular death. Glutathione creates a protective barrier that increases the strength of mitochondrial DNA. Through the same action, glutathione also protects another vulnerable part of the body's cells: the nucleus. Another intracellular benefit of glutathione is the elimination of free radicals. As the most powerful natural antioxidant, glutathione plays a major role in reducing free radical damage.
Glutathione :Boosting levels of known antioxidant may help resist age-related decline.
Glutathione :Boosting levels of known antioxidant may help resist age-related decline.A specific detoxification compound, glutathione, helps resist the toxic stresses of everyday life – but its levels decline with age and this sets the stage for a wide range of age-related health problems, scientists have discovered. What is this glutathione and how does it boosts health?
A new study, published in the journal Redox Biology, also highlighted a compound -- N-acetyl-cysteine, or NAC -- that is already used in high doses in medical detoxification emergencies. But the researchers said that at much lower levels NAC might help maintain glutathione levels and prevent the routine metabolic declines associated with aging. What is glutathione,and how does it ensure healthy living?
A diet rich in nuts improves sperm count and motility.
Improvements associated with better male fertility and explained by a reduction in sperm DNA fragmentation.The inclusion of nuts in a regular diet significantly improves the quality and function of human sperm, according to results of a randomized trial which measured conventional semen parameters and molecular changes over a 14-week study period.
The findings, say the investigators, 'support a beneficial role for chronic nut consumption in sperm quality' and reflect a research need for further male-specific dietary recommendations. The study was a 14-week randomized clinical trial in which 119 healthy young men aged 18-35 were allocated to either their usual western-style diet supplemented with 60 grams/day of mixed almonds, hazelnuts and walnuts, or their usual western-style diet without nuts.
In its analysis the study recorded not just sperm parameters (according to WHO benchmarks) but also changes in several molecular factors, including sperm DNA fragmentation.(3) Sperm and blood samples were analysed at baseline and after 14 weeks of intervention.
The findings, say the investigators, 'support a beneficial role for chronic nut consumption in sperm quality' and reflect a research need for further male-specific dietary recommendations. The study was a 14-week randomized clinical trial in which 119 healthy young men aged 18-35 were allocated to either their usual western-style diet supplemented with 60 grams/day of mixed almonds, hazelnuts and walnuts, or their usual western-style diet without nuts.
In its analysis the study recorded not just sperm parameters (according to WHO benchmarks) but also changes in several molecular factors, including sperm DNA fragmentation.(3) Sperm and blood samples were analysed at baseline and after 14 weeks of intervention.
RESEARCH:Take a coffee or tea break to protect your liver.
RESEARCH:Take a coffee or tea break to protect your liver.A new study indicates that drinking even a few cups a day may prevent hardening of the liver.Researchers found that drinking coffee and herbal tea may protect against liver fibrosis, estimated as the degree of liver stiffness, which is high in extensive scarring of the liver. Because these beverages are popular, widely available, and inexpensive, they could have the potential to become important in the prevention of advanced liver disease.
RESEARCH:Take a coffee or tea break to protect your liver. Chronic liver diseases rank as the 12th cause of death worldwide and many of these disorders are associated with unhealthy lifestyles. Conversely, a healthier lifestyle can help prevent or reverse liver disease. Liver-related mortality is closely related to the development of cirrhosis, the final consequence of progressive fibrosis, i.e. scarring of the liver resulting from chronic inflammation.
RESEARCH:Take a coffee or tea break to protect your liver. According to a new study published in the Journal of Hepatology, researchers found that drinking coffee and herbal tea may protect against liver fibrosis, estimated as the degree of liver stiffness, which is high in extensive scarring of the liver. Because these beverages are popular, widely available, and inexpensive, they could have the potential to become important in the prevention of advanced liver disease.
RESEARCH: Coffee consumption linked to decreased risk of colorectal cancer.
RESEARCH: Coffee consumption linked to decreased risk of colorectal cancer. Coffee consumption linked to decreased risk of colorectal cancer. Researchers have found that coffee consumption, including decaf, instant and espresso, decreases the risk of colorectal cancer. Moreover, these benefits increase the more coffee you drink.
RESEARCH: Coffee consumption linked to decreased risk of colorectal cancer. Whether you like your coffee black, decaf, half-caff or even instant, feel free to drink up. Researchers at the University of Southern California (USC) Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center of Keck Medicine of USC have found that coffee consumption decreases the risk of colorectal cancer.
RESEARCH: Coffee consumption linked to decreased risk of colorectal cancer. The study examined over 5,100 men and women who had been diagnosed with colorectal cancer within the past six months, along with an additional 4,000 men and women with no history of colorectal cancer to serve as a control group.
RESEARCH : Caffeine from four cups of coffee protects the heart with the help of mitochondria.
RESEARCH : Caffeine from four cups of coffee protects the heart with the help of mitochondria. A new study shows that a caffeine concentration equivalent to four cups of coffee promotes the movement of a regulatory protein into mitochondria, enhancing their function and protecting cardiovascular cells from damage.
RESEARCH : Caffeine from four cups of coffee protects the heart with the help of mitochondria. Caffeine consumption has been associated with lower risks for multiple diseases, including type II diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, but the mechanism underlying these protective effects has been unclear.
RESEARCH : Caffeine from four cups of coffee protects the heart with the help of mitochondria. The study now shows that caffeine promotes the movement of a regulatory protein into mitochondria, enhancing their function and protecting cardiovascular cells from damage.
Bacteria in female bladders.
Bacteria in female bladders.A new study has found that the female bladder not only contains bacteria, but the microbes are similar to those found in the vagina. The finding could lead to improved diagnostic tests and treatments for urinary tract infections and other urinary tract disorders.
Scientists and physicians at Loyola University Chicago and Loyola Medicine were the first to publish groundbreaking research that debunked the common belief that urine in healthy women is sterile.
Expanding on this finding, a new study published in Nature Communications has found that the bladder not only contains bacteria, but the microbes are similar to those found in the vagina. The new finding could lead to improved diagnostic tests and treatments for urinary tract infections and other urinary tract disorders.
Researchers sequenced the genes of 149 bacterial strains from 77 women. While the microbiota (community of microorganisms) found in the bladder and vagina were similar, they were markedly distinct from the microbiota found in the gastrointestinal tract.
New coronavirus emerges from bats in China, devastates young swine.
New coronavirus emerges from bats in China, devastates young swine. A newly identified coronavirus that killed nearly 25,000 piglets in 2016-17 in China emerged from horseshoe bats near the origin of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), which emerged in 2002 in the same bat species.
The new virus, called swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV), doesn't appear to infect people, unlike SARS-CoV which infected more than 8,000 people and killed 774. No SARS-CoV cases have been identified since 2004. The study investigators identified SADS-CoV on four pig farms in China's Guangdong Province.
More communication needed regarding disposal of pet pharmaceuticals.
More communication needed regarding disposal of pet pharmaceuticals.New research found that more than 60 percent of veterinary care professionals do not counsel their clients when it comes to the environmental stewardship aspect of medicine disposal.
New research from Oregon State University found that more than 60 percent of veterinary care professionals do not counsel their clients when it comes to the environmental stewardship aspect of medicine disposal -- findings that are troublesome but also represent an opportunity to dramatically reduce watershed contaminants.
"People are just starting to understand the impact that discarded pharmaceuticals and personal care products have on the environment," said the study's corresponding author, Jennifer Lam, who worked on the research while a graduate student in marine resource management at Oregon State University.
Dogs could be more similar to humans than we thought.
Dogs could be more similar to humans than we thought.Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than we previously thought, according to a new study.
Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than we previously thought, according to a study published in the open access journal, Microbiome. Dr Luis Pedro Coelho and colleagues from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory, in collaboration with Nestlé Research, evaluated the gut microbiome of two dog breeds and found that the gene content of the dogs microbiome showed many similarities to the human gut microbiome, and was more similar to humans than the microbiome of pigs or mice.
Dogs prefer to eat fat, and cats surprisingly tend toward carbs.
Dogs prefer to eat fat, and cats surprisingly tend toward carbs.Dogs gravitate toward high-fat food, but cats pounce on carbohydrates with even greater enthusiasm, according to research into the dietary habits of America's two most popular pets.
The study sheds new light on optimal nutrition for the animals and refutes a common notion that cats want and need a protein-heavy regimen.Findings were published this month in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
"The numbers were much different than what traditional thinking would have expected," said the study's corresponding author, Jean Hall, a professor in the Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University. "Some experts have thought cats need diets that are 40 or 50 percent protein. Our findings are quite different than the numbers used in marketing and are going to really challenge the pet food industry."
Dietary proteins contribute to a number of important physiological functions such as blood clotting, production of hormones and enzymes, vision and cell repair. Protein also has the most power to make the eater feel satiated; carbohydrates are No. 2 in that regard, followed by fat.
Human encouragement might influence how dogs solve problems.
Human encouragement might influence how dogs solve problems.A new study sheds light on how people influence animal behavior. Researchers evaluated the behavior of search and rescue dogs and pet dogs when presented with the same problem-solving task. Both sets of dogs persisted at the task for about the same proportion of time, but the search and rescue dogs were more successful at solving the task when encouraged by their owners.
Human encouragement might influence how dogs solve problems, according to a new Oregon State University study. The study, published in the journal Applied Animal Behaviour Science, sheds light on how people influence animal behavior, said study lead author Lauren Brubaker, a doctoral student in OSU's Human-Animal Interaction Lab.
Brubaker evaluated the behavior of search and rescue dogs and pet dogs when presented with the same problem-solving task. Both sets of dogs persisted at the task for about the same proportion of time, but the search and rescue dogs were more successful at solving the task when encouraged by their owners.
French bulldogs at risk of various health problems.
French bulldogs at risk of various health problems.French Bulldogs, predicted soon to become the most popular dog breed in the UK, are vulnerable to a number of health conditions, according to a new study published in the open access journal Canine Genetics and Epidemiology.
Researchers at The Royal Veterinary College (RVC), UK found that the most common issues in French Bulldogs over a one year period were ear infections, diarrhea and conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye surface).
Dr. Dan O'Neill, RVC Senior Lecturer and the main author, said: "French Bulldogs are a relatively new arrival to the list of common UK breeds so there is very little current research on them in the UK. Our study -- the first on this breed in the UK -- is based on anonymised records gathered from hundreds of UK vet clinics. It provides owners with information on the issues that they could expect and should look out for in French Bulldogs. It may also help potential new owners to decide if a French Bulldog really is for them."
Dr. O'Neill adds: "One of the interesting finding from our research is that male French Bulldogs appear to be less healthy than females. Males were more likely to get 8 of the 26 most common health problems while there were no issues that females were more likely to get than males."
How Nagana or Animal Trypanosomiasis is carried by tsetse flies .
How Nagana or Animal Trypanosomiasis is carried by tsetse flies . Researchers at the University of Bristol have revealed new details on how the animal disease Nagana is spread by tsetse flies in Africa. When animals are bitten by bloodsucking tsetse flies, they don't just get a painful bite, as the flies may be carrying a cargo of deadly microbes, trypanosomes.
These microbes are squirted into the skin of the animal as the fly feeds and invade the bloodstream, causing the severe and sometimes fatal disease Nagana or African Animal Trypanosomiasis. Most livestock are susceptible to this disease including cattle, sheep, goats, pigs and horses.
Tsetse flies pick up the microbes when they take blood from an infected animal. The blood is digested inside the gut of the fly, but the trypanosomes need to find their way back to the mouthparts so that they can be passed on to the next animal the fly bites.
Blinding canine eye disease.
Blinding canine eye disease.Discovery for a blinding canine eye disease reveals an unprecedented mode of inheritance.A new gene for canine congenital eye disease has been identified. Defective RBP4 leads to vitamin A deficiency and abnormal eye development during pregnancy. The study defines a novel recessive mode of maternal inheritance, which may underlie other types of birth defects.
Collaborating research groups from the University of Helsinki, UC Davis and the University of Jyväskylä describe a new genetic cause for canine congenital eye disease in Irish Soft-Coated Wheaten Terriers. The affected dogs suffer from bilateral microphthalmia i.e. very small eyes and anatomical defects, resulting in incurable blindness. Similar findings are seen in the Microphthalmia-Anophthalmia-Coloboma (MAC) spectrum of human congenital eye malformations, which are important causes of childhood blindness. RBP4 defect leads to vitamin A deficiency -- a known risk factor for eye diseases.
The study demonstrates a novel recessive mode of genetic inheritance, which has not described before. The researchers discovered that the dam's genotype determines the puppy's disease risk as both the dam and puppy must be homozygous for the mutation to manifest the disease.As a part of the research, a DNA test has been developed for veterinary diagnosis and breeding purposes. DNA testing is important for breeders to avoid producing more blind dogs. The test can identify carriers and allow better breeding plans.
Dogs can be a potential risk for future influenza pandemic.
Dogs can be a potential risk for future influenza pandemic.Dogs are a potential reservoir for a future influenza pandemic, according to a study published in the journal mBio. The study demonstrated that influenza virus can jump from pigs into canines and that influenza is becoming increasingly diverse in canines.
Influenza can jump among animal reservoirs where many different strains are located; these reservoirs serve as mixing bowls for the genetic diversity of strains. Pandemic influenza occurs when viruses jump from animal reservoirs to humans; with no prior exposure to the virus, most people do not have immunity to these viruses.
The main animal hosts for influenza are wild birds, poultry and other domestic birds in a species pack; swine; and horses. Some of the viral genes from the 2009 pandemic H1N1 virus originated in birds, from an avian virus that jumped to pigs, exchanged some of its genes with previously circulating swine viruses and then jumped from pigs into humans.
Birds and swine are major reservoirs of viral genetic diversity, whereas equines and canines have historically been restricted to one or two stable influenza A viruses lineages with no or very limited transmission to humans.
RESEARCH : Cattle, sheep and goats may transmit leptospirosis to humans in Tanzania.
RESEARCH : Cattle, sheep and goats may transmit leptospirosis to humans in Tanzania. Cattle, sheep and goats may transmit leptospirosis to humans in Tanzania. Leptospirosis, which affects more than one million people worldwide each year, is known to be transmitted to humans from a wide range of animals. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have discovered that more than 7 percent of the cattle and 1 percent of sheep and goats in local slaughterhouses in northern Tanzania are infected with Leptospira bacteria.
RESEARCH : Cattle, sheep and goats may transmit leptospirosis to humans in Tanzania. Leptospirosis is a disease caused by infection with bacteria of the genus Leptospira. In humans, the disease can range in severity from mild to severe disease leading to kidney damage, liver failure, or death. The disease is most common in tropical environments, but occurs worldwide, particularly in people who work outdoors or with animals. Acute leptospirosis is an important cause of febrile disease in Tanzania, where little is known about the most common sources of infection in humans.
In the new work conducted in northern Tanzania, Kathryn Allan, of the University of Glasgow, UK, and colleagues tested rodents, cattle, goats and sheep for Leptospira infection.
Sunday, July 1, 2018
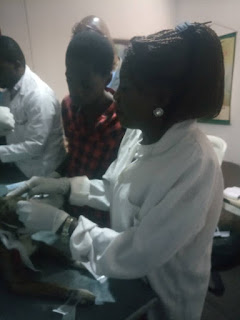
VETERINARY MEDICINE : WSAVA AND THE ONE CARE INITIATIVE.
VETERINARY MEDICINE : WSAVA AND THE ONE CARE INITIATIVE. WSAVA is World Small Animal Veterinary Association, with the primary purpose to advance the quality and availability of small animal medicine and surgery thus creating a unified standard of care for the benefit of animals and humankind.
VETERINARY MEDICINE : WSAVA AND THE ONE CARE INITIATIVE. WSAVA is a "Global Veterinary Community” creates a platform where veterinarians can help each other and to generate a “One global voice” from the veterinary profession to contribute to the world,the one care initiative. WSAVA represents more than 200,000 veterinarians worldwide through 105 member associations with a representation in Nigeria as well.
The Nigerian arm in conjunction with the WSAVA recently held a conference in Lagos with the theme "CONSOLIDATING YOUR PRACTICE SUCCESS" which featured series of lectures and wet lab. The WSAVA Vice President / Asia Siraya Chunekamrai was present to introduce the one care initiative.



















Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Agribusiness ideas.
Popular Posts
-
Five ways agriculture could benefit from artificial intelligence. Agriculture is the industry that accompanied the evolution of humanity ...
-
Funding opportunities for agricultural projects. International Tropical Timber Organization — Freezailah Fellowships 2017. ITTO makes grant...
-
The Ebola virus has taken its toll on countries in West Africa and some citizens outside west Africa. The virus is deadly and only prop...
-
A concerned citizen sent me this picture, he was wondering why these butchers were washing goats in this dirty water. A more intense look ...
-
Exploring New Horizons: Opportunities in the Leather Value Chain for Investors and Entrepreneurs. The leather industry has a long and rich ...
AGRIBUSINESS EDUCATION.
Translate
I-CONNECT -AGRICULTURE
AGRIBUSINESS TIPS.
AGRIBUSINESS.
The Agriculture Daily
veterinarymedicineechbeebolanle-ojuri.blogspot.com Cassava: benefits of garri as a fermented food. Cassava processing involves fermentation which is a plus for gut health. The fermentation process removes the cyanogenic glucosides present in the fres...







